Epoxy conductive adhesive
Jun 06, 2024
We all know that a separate epoxy resin is not conductive, how to make it with conductive properties, we all know that to conduct electricity, then you need a conductive medium, that epoxy conductive adhesive is the same reason, in the glue filled with randomly distributed metal or conductive carbon particles and other conductive media, so that epoxy resin with conductive properties.
Types of conductive adhesive
Generally speaking, conductive adhesive is composed of two parts: the matrix and conductive filler:
1. commonly used matrix including epoxy resin, silicone resin, polyimide resin, phenolic resin, polyurethane, acrylic resin and so on. Compared with other resins, epoxy resin has the advantages of good stability, corrosion resistance, low shrinkage, high bonding strength, bonding surface and good processability, therefore, epoxy resin is currently the most researched and widely used matrix materials.
2. conductive filler usually carbon, metal, metal oxide three categories. Conductive adhesive requires conductive particles itself to have good conductive properties, particle size should be in the appropriate range, can be added to the conductive adhesive matrix to form a conductive pathway. Conductive filler can be gold, silver, copper, aluminium, zinc, iron, nickel powder and graphite and some conductive compounds. Currently in actual production, the most widely used is silver powder.
The role of conductive adhesive
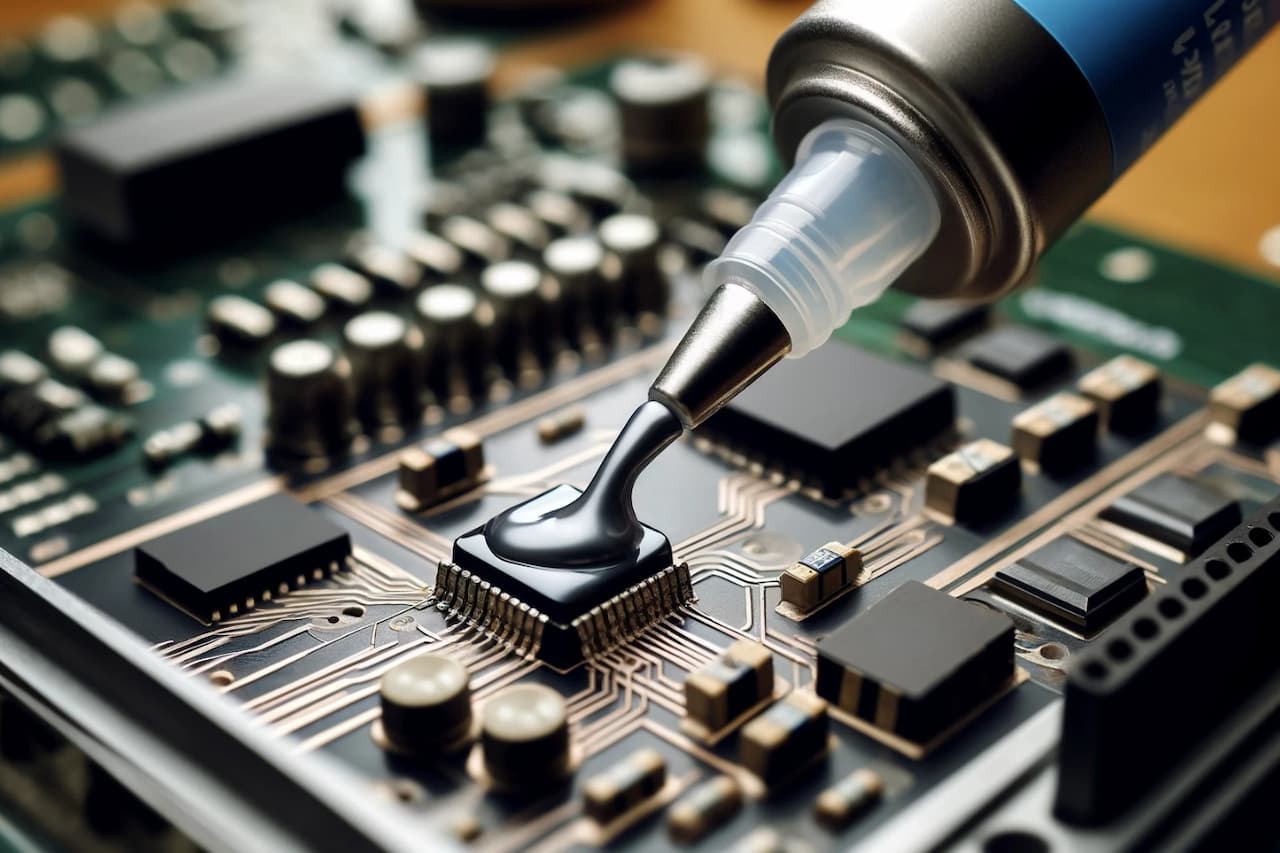
Epoxy resin conductive adhesive belongs to is non-polluting welding materials. Under normal circumstances epoxy resin is not conductive, but if the conductive silver paste and epoxy resin combination, their mixture can conduct electricity. Generally silver paste is the most common conductive filler, but materials such as gold, nickel, copper and carbon can also be used.
Another advantage of epoxy resins is that they are thermally conductive, which means they can cool electronic components. At present, many electronic components tend to be miniaturised, lightweight, highly integrated development, it is difficult to use a large number of welded materials to be made, if the use of conductive adhesive can be avoided the adverse effects of welding.
Epoxy resin conductive adhesive features
Has excellent adhesive strength. With all types of substrates can achieve good adhesion;
Formulation design is rich. With different curing agents, can prepare single-component adhesive or multi-component adhesive.
Room temperature curing, medium temperature curing and high temperature curing.
Good heat resistance;
Low curing shrinkage and stable properties;
Good chemical resistance.
The main application of epoxy resin conductive adhesive
Instead of solder for electronic components and printed circuit boards, glass, ceramic bonding, such as a variety of consumer electronics, communications equipment, automotive parts, industrial equipment, medical equipment, to solve the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and so on.
Electronic packaging: such as LCD, LED, integrated chips, printed circuit board components, ceramic capacitors and other electronic components and components of the package.
Photovoltaic panel bonding: to improve the defective rate of the cell due to solder, reduce costs and increase the photoelectric conversion rate.
Used as structural adhesive for bonding: metal-to-metal bonding, component lead bonding, battery terminal bonding.
Nanjing Yolatech provides all kinds of high purity and low chlorine epoxy resins, including Bisphenol A epoxy resin, Bisphenol F epoxy resin, Phenolic epoxy resin, Brominated epoxy resin, DOPO modified phenolic epoxy resin, MDI modified epoxy resin, DCPD epoxy resin, Multifunctional epoxy resin, Crystalline epoxy resin, HBPA epoxy resin and so on. And we also could provide all kinds of curing agents or hardeners and diluents.
We will be at your service 24 hours a day. Pls contact us freely.
Read More